QVQ-32B: The Open-Source LLM Taking on the Giants
The AI landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and increasingly, the focus is shifting from sheer model size to optimizing efficiency and performance. The recent release of QVQ-32B, a 32-billion parameter model developed by Qwen, Alibaba’s AI division, marks a significant milestone in this direction. Despite its relatively compact size, this new Chinese LLM is making headlines for delivering performance that rivals some of the largest models in the industry.
Open Source, but Also Available Online and via API
One of QVQ-32B’s most compelling aspects is its open-source nature. Released under the Apache 2.0 license, it’s available for download on platforms like Hugging Face and ModelScope. But what sets it apart is its accessibility: users can test it in real-time via a free web interface at chat.qwen.ai without needing high-end hardware. The interface feels familiar, mirroring the user experience of other leading LLMs.
QVQ-32B also includes a Thinking mode—similar to OpenAI’s O1 in ChatGPT and DeepSeek’s DeepThink—as well as a built-in web search feature that allows it to pull in real-time data for more accurate responses. The Thinking feature is particularly valuable, as it enables the model to process a query in multiple steps before responding, significantly improving the coherence and reliability of its answers.
This step-by-step reasoning is reminiscent of O1’s structured thought process, where the AI breaks down a prompt, refines its logic, and optimizes the final output. Instead of generating an instant reply, the model “pauses to think,” reducing errors and increasing precision—an essential capability for complex tasks like coding and advanced mathematics.
For developers looking to integrate it into their workflows, QVQ-32B is also available as an API on Together AI, offering one of the most cost-effective token-based pricing models currently available.
QVQ-32B vs. DeepSeek: How Do They Stack Up?
The real breakthrough here is how this “small” model manages to go toe-to-toe with DeepSeek R1, a Chinese LLM with a staggering 671 billion parameters. QVQ-32B is over 20 times smaller yet delivers comparable results. This is yet another example of why raw parameter count isn’t everything—efficiency and optimization are proving to be just as crucial as scale.
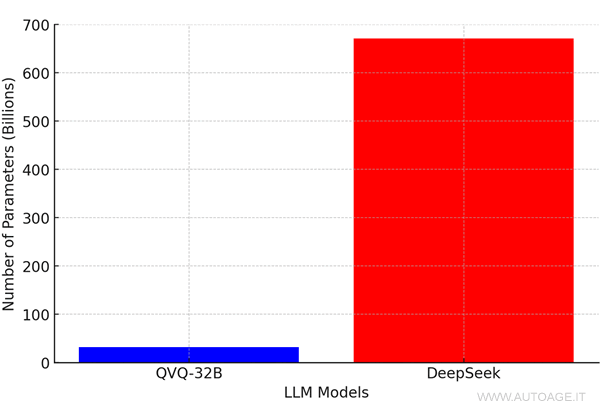
Digging into the numbers, benchmark results released by Qwen suggest that QVQ-32B matches or even surpasses DeepSeek R1 in several key areas. While independent verification will be essential, these early results highlight just how competitive QVQ-32B is—and signal the start of an intense rivalry between two of China’s top LLMs.
| Benchmark | QVQ-32B | DeepSeek R1 |
|---|---|---|
| MATH (Mathematical problems) | 79.1 | 79.5 |
| LiveCodeBench (Coding) | 63 | 65 |
| GSM8K (Mathematical reasoning) | 73.1 | 71.6 |
| IFEval (Following instructions) | 83.9 | 83.3 |
| BFCL (Function Calling) | 66.4 | 60.3 |
One of the standout results is in function calling—the model’s ability to interact with APIs and execute predefined functions. This capability enables real-time data retrieval, complex computations, and even device control, making it a key feature for integrating AI into real-world applications. Here, QVQ-32B significantly outperforms DeepSeek R1, demonstrating a clear advantage in software integration and task execution.
How Can a Smaller Model Compete with Larger LLMs?
QVQ-32B’s impressive performance boils down to its advanced use of Reinforcement Learning applied to a pre-trained model, allowing it to refine its responses and reasoning without the need for more parameters. The secret to its efficiency lies in its training methodology, which unfolds in three key stages:
- Pretraining on a massive dataset to build a strong foundational knowledge base.
- Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning on mathematics and coding to enhance logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
- Optimization through a Rule-Based System that helps the model prioritize the most effective reasoning pathways.
This approach not only enhances response accuracy but also strengthens the model’s ability to follow complex instructions (instruction following) and align with human preferences (instruction alignment).
The U.S.-China AI Race: A New Challenger Emerges
QVQ-32B is a prime example of how efficiency and optimization are now more critical than brute-force scaling. With a well-calibrated training process and cutting-edge Reinforcement Learning techniques, this 32-billion parameter model manages to compete—and in some cases, outperform—massive-scale models, all while maintaining a lean and cost-efficient structure.
As an open-source, free, and widely accessible model, QVQ-32B is poised to become a serious contender in the AI landscape, offering high-end capabilities at a fraction of the cost. Its ability to handle function calling, execute precise instructions, and integrate seamlessly with external systems makes it particularly promising for real-world applications.
With the AI arms race heating up, it will be fascinating to see how major players like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google respond—whether by pushing for more efficient models, slashing costs, or rolling out new innovations. For now, QVQ-32B is yet another sign that China is closing the gap with the U.S. in the LLM space, proving that smart optimization can rival even the most computationally intensive approaches.
Andrea Minini